Introduction
The vulnerability of ZeroLogon or CVE-2020-1742 is an extremely dangerous vulnerability in all versions of Windows servers from 2008 to 2019, which has the maximum level of danger (CVSS 10/10). By using this vulnerability, an intruder can easily get domain admin access, with no need for any authentication, and only by sending a few bytes to the DC server.
Unfortunately, since:
- The using code of this vulnerability is available to attackers,
- Using vulnerability is very simple, without problems, and with no need for any authentications or…
- All versions of the Windows server are vulnerable.
- Vulnerability provides the maximum imaginable access (general domain admin) for the attacker,
- There is no possibility to close the DC port and for the active directory to be active, this port must be accessible from all network systems.
- And due to the vulnerability in MS-NPRC, is not easily attachable (simply installing a Windows update for protection is not enough), and installing a patch could result in some disorders in domain performance,
This vulnerability alone maybe is the most dangerous and immediate in the year 2020 network managers must install the patch and fix it, as soon as possible.
The details of the vulnerability
To completely understand this vulnerability, first, need to know a few things about MS-NRPC protocol. This protocol is an RPC interface that is used for the following:
- Authenticate domain users
- Authenticate the domain-based systems
- Connections between domain controllers of a domain
- Forest connections
- Performing all operations such as changing domain systems passwords
- Finding and managing these connections and …
As it is obvious, closing or limiting this protocol is not possible due to its applications.
The vulnerability of ZeroLogon or CVE-2020-1472 occurred due to a defect in setting up the method of the AES-CFB8 algorithm in MS-NRPC during user authentication. By sending some MS-NRPC packets that include zero-value-8-byte authentication data, the intruder can change his access to the network admin address and then change the DC password. AES-CFB8 algorithm had a 16-byte Initial Vector (IV) which is essential and should fill with a random value each time, but unfortunately, in Microsoft MS-NRPC protocol, the IV value is always considered equal to 16-byte-zero. This problem makes AES-CFB8 vulnerable in cryptography, and intruders, on average, can simply confuse the server after sending a packet that includes 8-byte-zero 256 times as authentication data and receive the maximum access level from the server.
How to test for vulnerabilities
How to test the Windows domain name for vulnerabilities is as follows:
- First, download and install Python 3 software (python.org)
- Then install the “impacket” module, by running this order-pip install packet
- Download the testing tool of zerologon_tester.py from (https://github.com/SecuraBV/CVE-2020-1472/raw/master/zerologon_tester.py)
- By opening “command line”, go to the folder that contains zerologon_tester.py
- Run follow the order by replacing proper values to DC-Name and DC-IP: python3 zerologon_tester.py <DC-Name> <DC-IP>
- Note that step 5 must be executed for all DCs (even DCs that are in read-only status).
- In case that test is executed correctly, you will receive one of the two following messages.
- In case you encounter a timeout with no (=) sign, it means that Padvish has detected and blocked this attack.
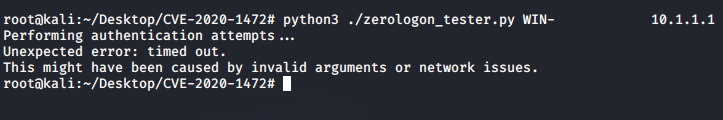
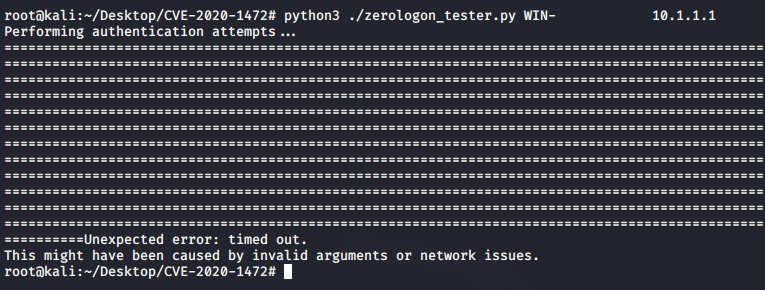
- In case you encounter a timeout after so many (=) signs, it means that your system is not vulnerable.
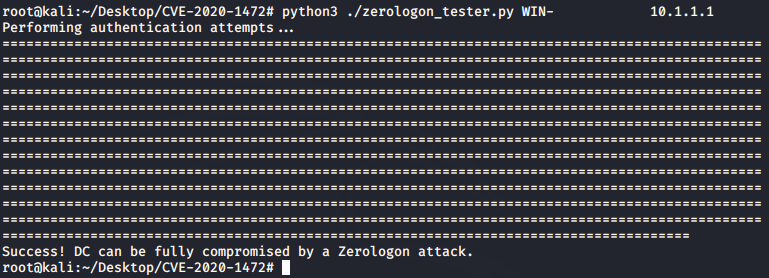
- The message: “Success! DC can be fully compromised by a ZeroLogon attack” means the vulnerability of the domain and you need to patch the vulnerability.
How to fix the vulnerability and install the patch
For the ZeroLogon vulnerability, simply updating Windows and installing a patch is not enough to fix it.
- Update the DC systems
- Check the Windows logs and find incompatible systems
- Update or exclude the incompatible signals
- Enable the secure connection mode
Since this defect is in the MS-NRPC connection protocol and fixing it needs to change the protocol, patch installation may be incompatible with some equipment and software. So despite other vulnerabilities, only installing a patch to fix it is not enough and the 4 steps process (installing a patch, finding incompatible systems, fixing the problem, complete patch activation) must be performed. Otherwise, installing a patch alone, cannot block this dangerous vulnerability.
The 4 steps of securing a network are:
- Update: on august 11 2020 Microsoft released an update for this type of vulnerability. To install go to follow the link and download the proper update from the relevant table: https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2020-1472
- Check: some old systems, may use old protocols. So, after installing the update, go to Event Viewer in DC and Windows security logs checking section, and find the systems use an incompatible and not secure connection to connect with DC. For this matter, you can filter and check incidents with event ID5829 By executing the script on collected logs, you can detect all systems that have an incompatible and not secure connection to connect DC: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4557233/script-to-help-in-monitoring-event-ids-related-to-changes-in-netlogon
- Fixing: in the next step, it needs to update the discovered systems in the previous step to the last version, or add them to the exceptions list of Group Policy, which naturally will make them insecure.
- Complete activation: enabling the Enforcement Mode option to activate full protection, and stop insecure connections.
For this matter, you must create a DWORD value type with the FullSecureChannelProtection name in the HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Netlogon\Parameters path and set it to 1.
It should be noted that as Microsoft said, a final patch for this vulnerability will be released during the first 3 months of the year 2021, and its installation is essentially to completely fix the danger of this vulnerability.
How does Padvish block this vulnerability?
However, installing the patch is the most certain and definite way to prevent this vulnerability and it must be done, but Padvish anti-virus will detect and prevent all connected connections that user authentication data which all of its bytes are valued at zero, by its IPS mechanism. You can refer to the Padvish IPS server to view relevant logs of this attack that Padvish detects and prevent as an Exploit.ZeroLogon.possibility and also for systems that are probably attacking to DC Server, refer to the IPS reports tab of the anti-virus.